nodejs-project-structure
原文地址 https://www.softwareontheroad.com/ideal-nodejs-project-structure/?utm_source=github&utm_medium=readme
Bulletproof node.js project architecture 🛡️
Update 04/21/2019: Implementation example repository
Express.js is great frameworks for making a node.js REST APIs however it doesn't give you any clue on how to organizing your node.js project.
While it may sound silly, this is a real problem.
The correct organization of your node.js project structure will avoid duplication of code, will improve stability, and potentially, will help you scale your services if is done correctly.
This post is extense research, from my years of experience dealing with a poor structured node.js project, bad patterns, and countless hours of refactoring code and moving things around.
If you need help to align your node.js project architecture, just drop me a letter at sam@softwareontheroad.com
- The folder structure 🏢
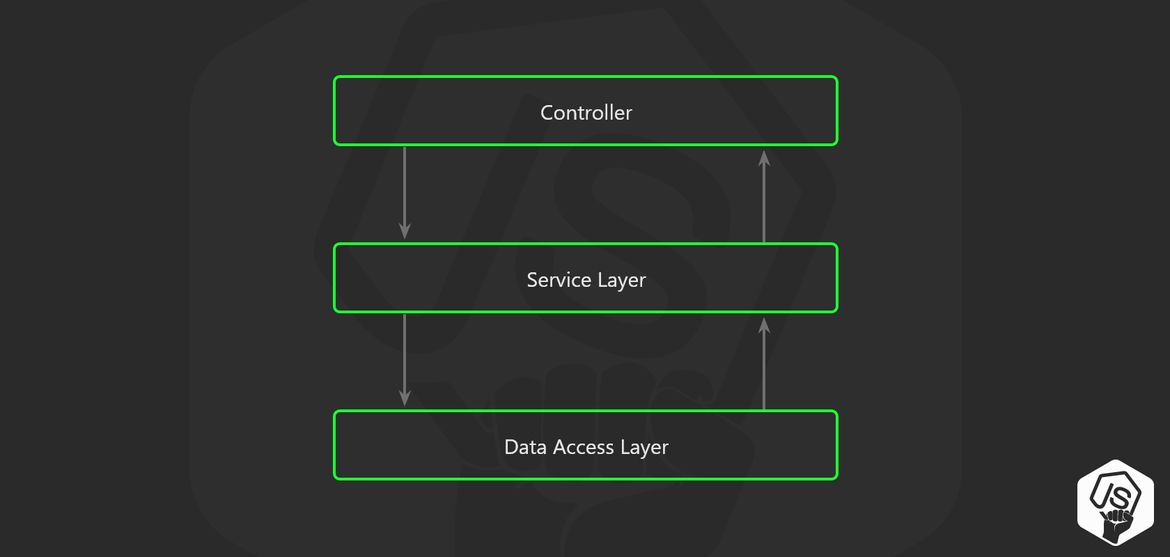
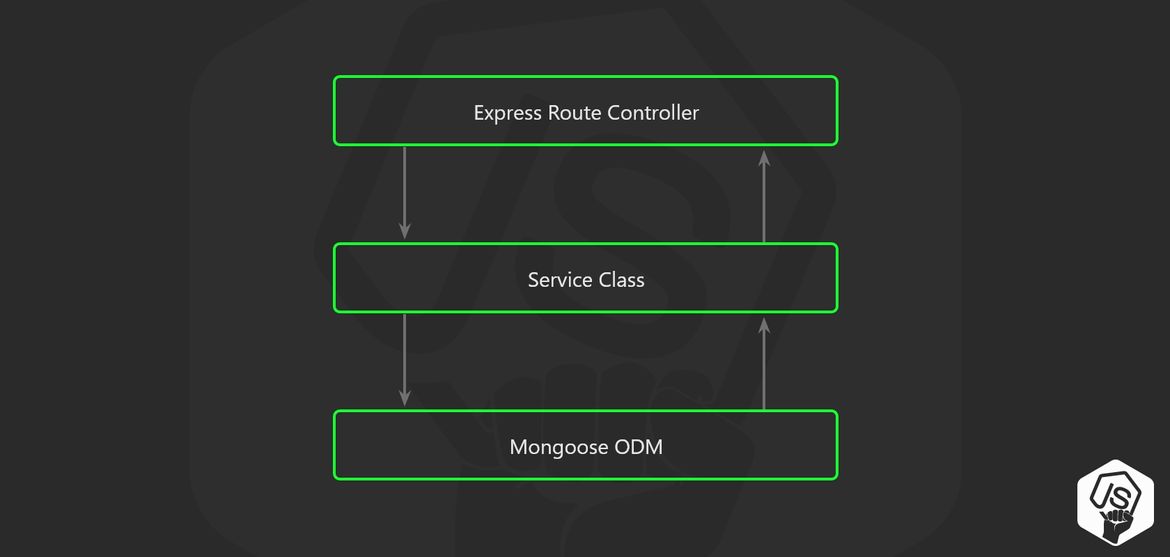
- 3 Layer architecture 🥪
- Service Layer 💼
- Pub/Sub Layer ️️️️🎙️️
- Dependency Injection 💉
- Unit Testing 🕵🏻
- Cron Jobs and recurring task ⚡
- Configurations and secrets 🤫
- Loaders 🏗️
- Example repository
Here is the node.js project structure that I'm talking about.
I use this in every node.js REST API service that I build, let's see in details what every component do.
src |
It is more than just a way of ordering javascript files...
The idea is to use the principle of separation of concerns to move the business logic away from the node.js API Routes.
Because someday, you will want to use your business logic on a CLI tool, or not going far, in a recurring task.
And make an API call from the node.js server to itself it's not a good idea...
☠️ Don't put your business logic inside the controllers!! ☠️
You may be tempted to just use the express.js controllers to store the business logic of your application, but this quickly becomes spaghetti code, as soon as you need to write unit tests, you will end up dealing with complex mocks for req or res express.js objects.
It's complicated to distingue when a response should be sent, and when to continue processing in 'background', let's say after the response is sent to the client.
Here is an example of what not to do.
route.post('/', async (req, res, next) => { |
Use a service layer for your business logic
This layer is where your business logic should live.
It's just a collection of classes with clear purposes, following the SOLID principles applied to node.js.
In this layer there should not exists any form of 'SQL query', use the data access layer for that.
Move your code away from the express.js router
Don't pass the req or res object to the service layer
Don't return anything related to the HTTP transport layer like a status code or headers from the service layer.
Example
route.post('/', |
Here is how your service will be working behind the scenes.
import UserModel from '../models/user'; |
Use a Pub/Sub(Publish–subscribe pattern) layer too
在软件架构中,发布/订阅(Publish–subscribe pattern)是一种消息范式,消息的发送者(称为发布者)不会将消息直接发送给特定的接收者(称为订阅者)。而是将发布的消息分为不同的类别,无需了解哪些订阅者(如果有的话)可能存在。同样的,订阅者可以表达对一个或多个类别的兴趣,只接收感兴趣的消息,无需了解哪些发布者(如果有的话)存在。
The pub/sub pattern goes beyond the classic 3 layer architecture proposed here but it's extremely useful.
The simple node.js API endpoint that creates a user right now, may want to call third-party services, maybe to an analytics service, or maybe start an email sequence.
Sooner than later, that simple "create" operation will be doing several things, and you will end up with 1000 lines of code, all in a single function.
That violates the principle of single responsibility.
So, it's better to separate responsibilities from the start, so your code remains maintainable.
import UserModel from '../models/user'; |
An imperative call to a dependent service is not the best way of doing it.
A better approach is by emitting an event i.e. 'a user signed up with this email'.
And you are done, now it's the responsibility of the listeners to do their job.
import UserModel from '../models/user'; |
Now you can split the event handlers/listeners into multiple files.
eventEmitter.on('user_signup', ({ user, company }) => { |
eventEmitter.on('user_signup', async ({ user, company }) => { |
eventEmitter.on('user_signup', async ({ user, company }) => { |
You can wrap the await statements into a try-catch block or you can just let it fail and handle the 'unhandledPromise' process.on('unhandledRejection',cb)
Dependency Injection
D.I. or inversion of control (IoC) is a common pattern that will help the organization of your code, by 'injecting' or passing through the constructor the dependencies of your class or function.
By doing this way you will gain the flexibility to inject a 'compatible dependency' when, for example, you write the unit tests for the service, or when the service is used in another context.
Code with no D.I
import UserModel from '../models/user'; |
Code with manual dependency injection
export default class UserService { |
Now you can inject custom dependencies.
import UserService from '../services/user'; |
The amount of dependencies a service can have is infinite, and refactor every instantiation of it when you add a new one is a boring and error-prone task.
That's why dependency injection frameworks were created.
The idea is you declare your dependencies in the class, and when you need an instance of that class, you just call the 'Service Locator'.
Let's see an example using typedi an npm library that brings D.I to node.js
You can read more on how to use typedi in the official documentation
WARNING typescript example
import { Service } from 'typedi'; |
services/user.ts
Now typedi will take care of resolving any dependency the UserService require.
import { Container } from 'typedi'; |
Abusing service locator calls is an anti-pattern
Using Dependency Injection with Express.js in Node.js
Using D.I. in express.js is the final piece of the puzzle for this node.js project architecture.
Routing layer
route.post('/', |
Awesome, project is looking great ! It's so organized that makes me want to be coding something right now.
An unit test example
By using dependency injection and these organization patterns, unit testing becomes really simple.
You don't have to mock req/res objects or require(...) calls.
Example: Unit test for signup user method
tests/unit/services/user.js
import UserService from '../../../src/services/user'; |
Cron Jobs and recurring task
So, now that the business logic encapsulated into the service layer, it's easier to use it from a Cron job.
You should never rely on node.js setTimeout or another primitive way of delay the execution of code, but on a framework that persist your jobs, and the execution of them, in a database.
This way you will have control over the failed jobs, and feedback of those who succeed. I already wrote on good practice for this so, check my guide on using agenda.js the best task manager for node.js.
Configurations and secrets
Following the battle-tested concepts of Twelve-Factor App for node.js the best approach to store API Keys and database string connections, it's by using dotenv.
Put a .env file, that must never be committed (but it has to exist with default values in your repository) then, the npm package dotenv loads the .env file and insert the vars into the process.env object of node.js.
That could be enough but, I like to add an extra step. Have a config/index.ts file where the dotenv npm package loads the .env file and then I use an object to store the variables, so we have a structure and code autocompletion.
config/index.js
const dotenv = require('dotenv'); |
This way you avoid flooding your code with process.env.MY_RANDOM_VAR instructions, and by having the autocompletion you don't have to know how to name the env var.
Loaders
I took this pattern from W3Tech microframework but without depending upon their package.
The idea is that you split the startup process of your node.js service into testable modules.
Let's see a classic express.js app initialization
const mongoose = require('mongoose'); |
As you see, this part of your application can be a real mess.
Here is an effective way to deal with it.
const loaders = require('./loaders'); |
Now the loaders are just tiny files with a concise purpose
loaders/index.js
import expressLoader from './express'; |
The express loader
loaders/express.js
import * as express from 'express'; |
The mongo loader
loaders/mongoose.js
import * as mongoose from 'mongoose' |
Conclusion
We deep dive into a production tested node.js project structure, here are some summarized tips:
Use a 3 layer architecture.
Don't put your business logic into the express.js controllers.
Use PubSub pattern and emit events for background tasks.
Have dependency injection for your peace of mind.
Never leak your passwords, secrets and API keys, use a configuration manager.
Split your node.js server configurations into small modules that can be loaded independently.
See the example repository here
Get the latest articles in your inbox.
Join the other 2000+ savvy node.js developers who get article updates. You will receive only high-quality articles about Node.js, Cloud Computing and Javascript front-end frameworks.